Painless flu jab patch for people scared of injections
- Published
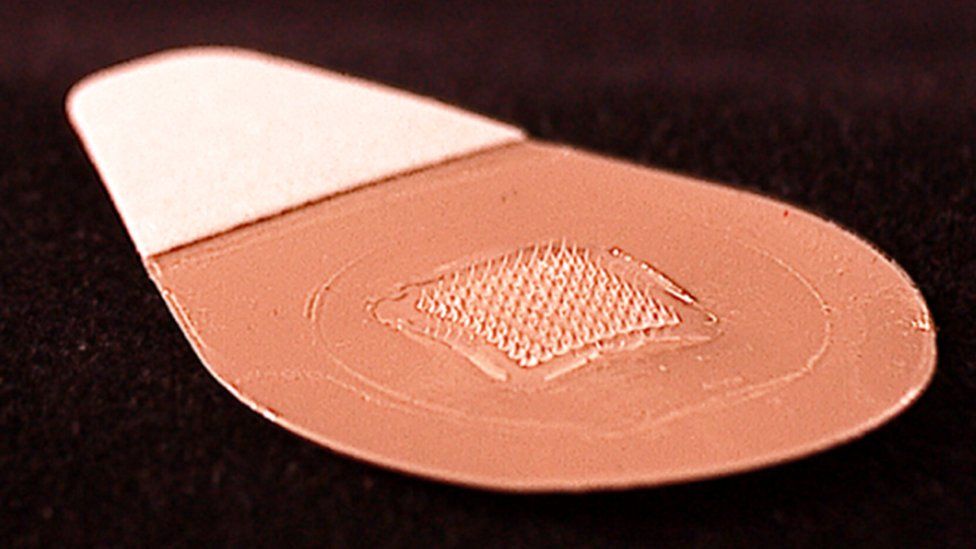
A 'painless' sticking plaster flu jab that delivers vaccine into the skin has passed important safety tests in the first trial in people.
The patch has a hundred tiny hair-like microneedles on its adhesive side that penetrate the skin's surface.
It is simple enough for people to stick on themselves.
That should help more people get immunised, including those who are scared of injections, experts told the Lancet journal .
Bye bye injections
Unlike the standard flu jab, it doesn't need to be kept in the fridge, meaning pharmacies could easily stock it on their shelves for people to buy.
Volunteers who tested it said they preferred it to injections.
It offers the same protection as a regular vaccine, but without pain, according to its developers from Emory University and the Georgia Institute of Technology, who are funded by the US National Institutes of Health.
The patch punctures the uppermost layers of the skin, whereas regular flu injections go all the way through and into muscle.
Lead researcher Prof Mark Prausnitz, who is also part of a company that wants to license the technology, said: "If you zoom in under the microscope what you'll see are microscopically small needles. They puncture painlessly into the skin."
His team tested the patch alongside flu injections. Some of the 100 volunteers got the regular shot in the arm, while others applied the microneedle patch to their wrist for 20 minutes.
Most said using the patch was painless, but some experienced mild side effects - redness, itching and tenderness in the area of skin area where it had been applied. These symptoms got better on their own over days.
Easy to use
Experts say the patch could revolutionise how flu and other vaccines are given, although more clinical tests over the next few years are needed to get the patch system approved for widespread use.
Dr Nadine Rouphael, from Emory University, said: "We could envisage vaccination at home, in the workplace or even via mail distribution."
The patch can be thrown in the bin after it is used because the microneedles dissolve away.
And because it can be safely stored for up to a year without refrigeration, it could prove extremely useful in the developing world.
Experts from Public Health England said it might also be good to use in young children, who tend not to like needles, although the UK has already introduced a nasal spray flu vaccine for them.
John Edmunds, an expert in infectious diseases at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, said: "This study is undoubtedly an important step towards a better way to deliver future vaccines."
Other researchers have also been looking at pain-free skin delivery. A flu shot syringe that uses a microneedle has already been approved for use in the US.
Scientists in Australia have been designing a nanopatch with even smaller needles.
Follow Michelle on Twitter
- Published28 January 2016
- Published24 August 2015