Coronavirus bailouts: Which country has the most generous deal?
- Published

Can rescue spending clean up the global economy?
Coronavirus shutdowns around the world have pushed countries into crisis-mode, prompting a massive rescue spending in an effort to soften the blow from what is expected to be the worst economic contraction since the 1930s.
As of 7 April, countries around the world had approved more than $4.5tn worth of emergency measures, according to the IMF. That figure has only grown in the weeks since.
So how do the responses compare?
New spending
Columbia economics professor Ceyhun Elgin has been working with colleagues around the world to track the responses in 166 countries.
By his calculations, Japan's response has been among the most aggressive, with a spending package estimated at roughly 20% of the country's economy. (It is topped only by Malta, which benefits from European Union funds.)
That compares to rescue spending estimated at roughly 14% of GDP in the US, 11% in Australia, 8.4% in Canada, 5% in the UK, 1.5% in Colombia and 0.6% in Gambia.
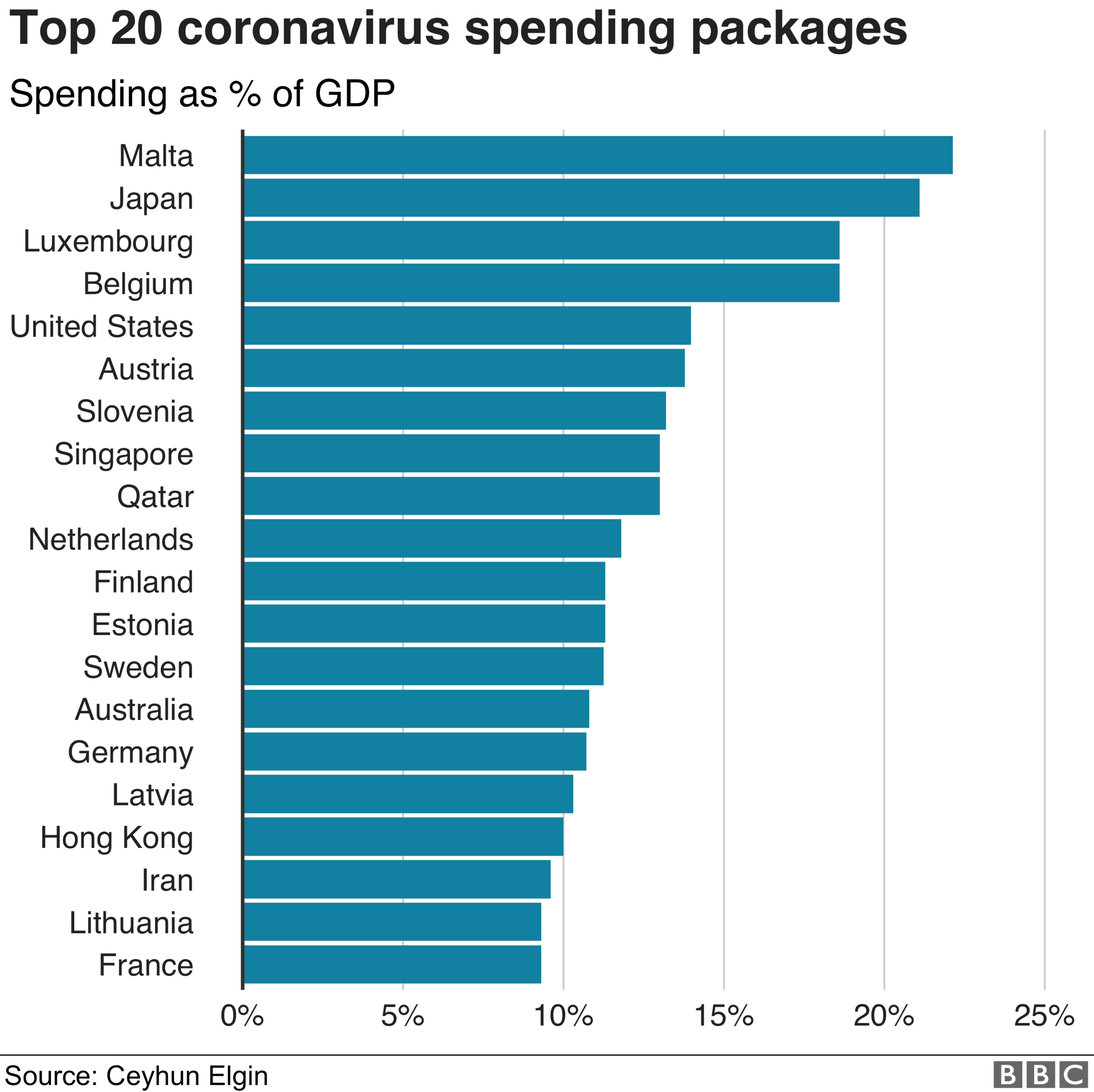
But that ranking looks different if measures beyond spending, such as central bank actions, are considered.
In the biggest European countries, for example, government pledges to guarantee new loans provided to businesses hurt by the shutdowns - a move meant to keep banks lending and stave off bankruptcies - has accounted for a major part of the response.
America's central bank has also stepped in with lending programmes with a similar aim.
Factoring in those kinds of actions puts France at the top of the pack and moves the UK into fifth place, instead of 47th.
Prof Elgin says the biggest responses have occurred in countries that are richer, older - and have fewer hospital beds. Countries like the US and Japan are also in a better position to finance new spending, since investor willingness to buy their bonds means they benefit from low borrowing costs.
However Prof Elgin says size shouldn't be mistaken for effectiveness, noting that countries are deploying funds differently.
"All the different contents in these packages, they might have different multiplier effects, creating different outcomes," he says.
Relief directed at companies tends to be a phenomenon of "advanced economies", says Paolo Mauro, deputy director of the IMF's fiscal affairs department. While the sums involved are potentially significant, he says such programmes tend to be relatively low risk, since many firms will be able to repay the loans as planned.
Meanwhile, some poorer countries have prepared responses, but will need to get money from international organisations and other donors to execute.

India's rescue effort includes rice and beans for the poor
Direct payments
Some strategies can be found in relief plans around the world, such as cash transfers.
In many countries, the aid is targeted at the poor or people working in the informal economy and unlikely to get assistance through other programmes; or else conditioned on a person's job having been affected by shutdowns.
Canada, for example, is providing CAD 2,000 (£1,150; $1,400) per month for up to four months to those who have lost income due to the pandemic, while Costa Rica is funding a monthly allowance of $220 (£177) for people who have lost their jobs due to the virus.
The US and some countries in Asia have taken an even broader approach.
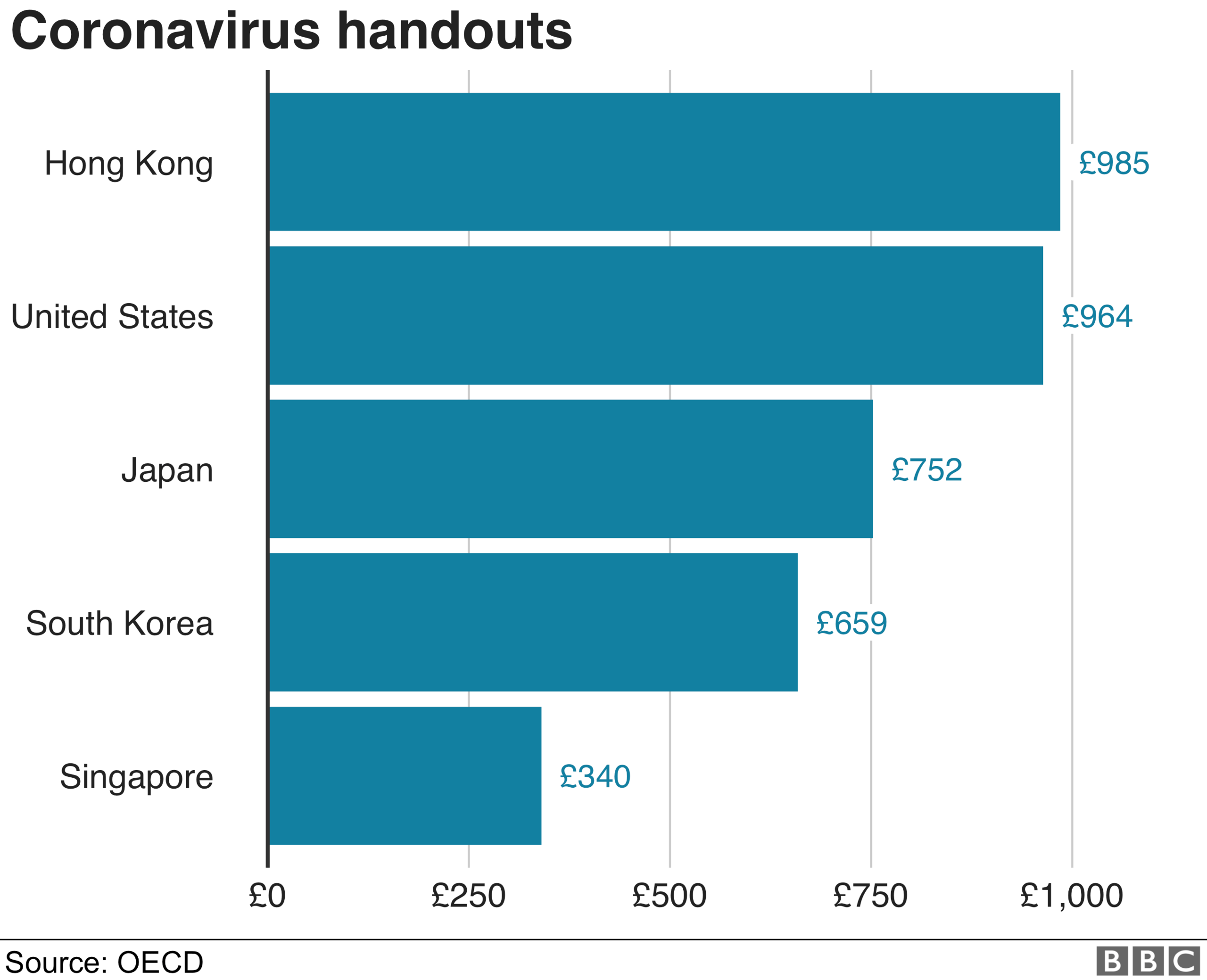
All Americans earning under $99,000 - an estimated 90% of households - are due to receive as much as $1,200 (£964) per adult, while South Korea's central government is sending cheques of up to KRW 1 million (£659; $820) to families in the bottom 70% income bracket.
Hong Kong in February announced a handout of $10,000 Hong Kong dollar ($1,280; £985) per adult; Japan is sending its citizens JPY 100,000 (£752; $931) per person, and Singapore $S600 (£340; $422).
In Europe, in contrast, many countries have opted against one-off bonuses and are relying on relatively strong existing safety net programmes, like the UK's Universal Credit, to meet the increased needs.
"The difference is in what economists call the automatic stabilisers," says Mr Mauro of the IMF. "The discretionary response is very large in the United States but when you're comparing you need to take into account that actually more needs to be done in the US because the social safety nets are smaller."
The American families falling off a financial cliff
Wage subsidies
Another common strategy has been government programmes that help cover payrolls for companies suffering from lockdown measures. The hope is that if firms retain staff it will help the economy bounce back more quickly once the restrictions are lifted.
The Netherlands has put forward one of the most generous plans, pledging to replace up to 90% of wage costs for eligible companies, while France is offering to cover 84% of the gross wage - and up to 100% if a worker makes minimum wage.
The UK's scheme will pay 80% of earnings of furloughed staff up to £2,500 per employee per month, for at least three months, while Canada will cover 75% of wages for up to three months.
Many of these plans build on existing "short-term work" programmes.
The US, where such programmes were not already widespread, has taken a less direct approach, dedicating more than $650bn to business loans, which do not have to be repaid if firms maintain staffing levels and spend the majority on wages within two months.
The so-called the Paycheck Protection Program has been overwhelmed by demand but it has also been roiled in controversy. There has been widespread outcry about large companies sucking up much of the money, which had been pitched as relief for small businesses.
Other firms have criticised the rules focusing the spending on payrolls, arguing that it is other expenses that threaten their survival, while low-wage staff may be better off receiving newly expanded unemployment benefits.

Many relief efforts are struggling to reach people working in the informal economy
Providing wage subsidies makes sense if the shutdowns are brief, says Daniel Bunn, vice-president of global projects at the Tax Foundation, a Washington think tank. But they are likely to be less effective if they persist, and significantly alter the contours of the economy.
"The challenge is not knowing how long the economic shutdown is going to last or what position businesses or families or workers will be in on the other side of this," he says.
For now, he says many countries with the funds on hand have decided to err on the side of doing too much - and it's too early to tell whether even that will be enough.

A SIMPLE GUIDE: How do I protect myself?
AVOIDING CONTACT: The rules on self-isolation and exercise
HOPE AND LOSS: Your coronavirus stories
LOOK-UP TOOL: Check cases in your area
TESTING: Can I get tested for coronavirus?

- Published23 April 2020

- Published24 April 2020

- Published3 April 2020
